Buffer
简介
A container for data of a specific primitive type. A buffer is a linear, finite sequence of elements of a specific primitive type. Aside from its content, the essential properties of a buffer are its capacity, limit, and position.
- A buffer’s capacity is the number of elements it contains. The capacity of a buffer is never negative and never changes.
- A buffer’s limit is the index of the first element that should not be read or written. A buffer’s limit is never negative and is never greater than its capacity.
- A buffer’s position is the index of the next element to be read or written. A buffer’s position is never negative and is never greater than its limit.
一种用于特定基本类型的数据容器。缓冲区是一个特定的基本类型的元件的线性,有限序列。 除了其内容,缓冲的基本性质是它的容量,限制和位置:
- 缓冲区的容量是它所包含的元素数量。 缓冲区的容量从不为负,从来没有改变。
- 缓冲区的限制是不应读取或写入的第一个元素的索引。 缓冲区的限制是从不为负,并且永远不会比它更大的容量。
- 缓冲区的位置要被读出或写入的下一个元素的索引。 缓冲区的位置永远不会为负,并且永远不会比它的极限。
在NIO中有8种缓冲区类,分别如下:ByteBuffer、CharBuffer、DoubleBuffer、FloatBuffer、IntBuffer、LongBuffer、ShortBuffer、MappedByteBuffer。MappedByteBuffer是专门用于内存映射的一种ByteBuffer类型。
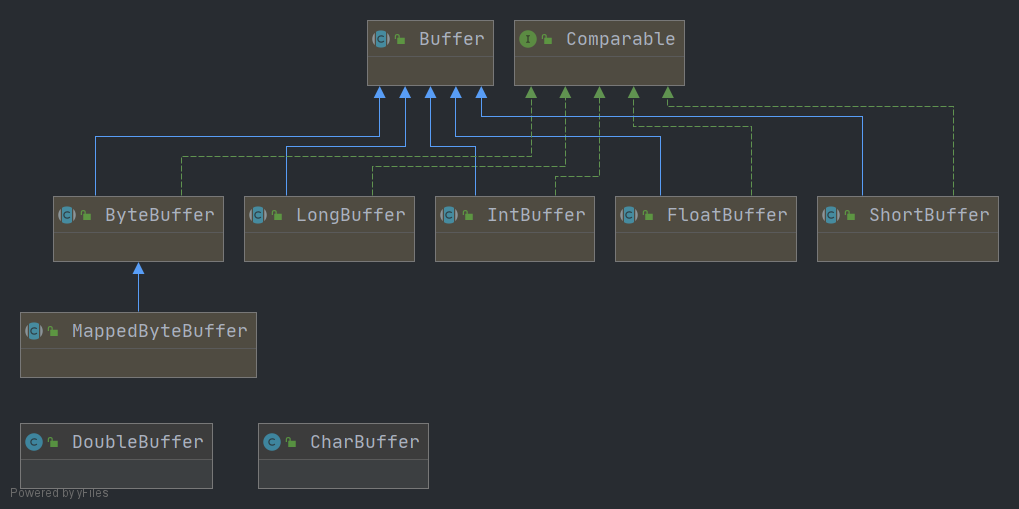
属性
Buffer的重要成员属性分别是:capacity(容量)、position(读写位置)、limit(读写的限制)。此外标记属性为:mark(标记),可以将当前position临时存入mark中;需要的时候从mark标记恢复position位置。
1
2
3
4
5
// Invariants: mark <= position <= limit <= capacity
private int mark = -1;
private int position = 0;
private int limit;
private int capacity;
| 属性 | 说明 | | ———— | ———— | | capacity | 容量,即可以容纳的最大数据量;在缓冲区创建时设置并且不能改变 | | limit | 上限,缓冲区中当前的数据量| | position | 位置,缓冲区中下一个要被读或些的元素的索引| | mark | 调用mark()方法来设置mark=position,再调用reset()可以让position恢复到mark标记的位置,即position=mark |
capacity
Buffer类的capacity属性,表示内部容量的大小。一旦写入的对象数量超过了capacity容量,缓冲区就满了,不能再写入了。 Buffer类的对象在初始化时,会按照capacity分配内部的内存。在内存分配好之后,大小不在改变。capacity容量不是指内存块byte[]数组的字节的数量,capacity容量指的是写入的数据对象的数量。
position
Buffer类的position属性,表示当前的位置。position属性与缓冲区的读写模式有关。在不同的模式下,position属性的值是不同的。当缓冲区进行读写的模式改变时,position会进行调整。
- 在写入模式下,position的值变化:
- 在刚进入到写模式时,position值为0,表示当前的写入位置为从头开始。
- 每当一个数据写到缓冲区之后,position会向后移动到下一个可写的位置。
- 初始的position值为0,最大可写值position为limit– 1。当position值达到limit时,缓冲区就已经无空间可写了。
- 在读模式下,position的值变化:
- 当缓冲区刚开始进入到读模式时,position会被重置为0。
- 当从缓冲区读取时,也是从position位置开始读。读取数据后,position向前移动到下一个可读的位置。
- position最大的值为最大可读上限limit,当position达到limit时,表明缓冲区已经无数据可读。
limit
Buffer类的limit属性,表示读写的最大上限。limit属性,也与缓冲区的读写模式有关。在不同的模式下,limit的值的含义是不同的。
- 在写模式下,limit属性值的含义为可以写入的数据最大上限。在刚进入到写模式时,limit的值会被设置成缓冲区的capacity容量值,表示可以一直将缓冲区的容量写满。
- 在读模式下,limit的值含义为最多能从缓冲区中读取到多少数据。
方法
allocate(int capacity)
Buffer使用之前要分配内存空间,使用allocate(int capacity)创建缓冲区。ByteBuffer#allocate(int capacity)示例如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
public static ByteBuffer allocate(int capacity) {
if (capacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
//new一个ByteBuffer的子类HeapByteBuffer对象
return new HeapByteBuffer(capacity, capacity);
}
HeapByteBuffer(int cap, int lim) { // package-private
super(-1, 0, lim, cap, new byte[cap], 0);
/*
hb = new byte[cap];
offset = 0;
*/
}
ByteBuffer(int mark, int pos, int lim, int cap, // package-private
byte[] hb, int offset)
{
super(mark, pos, lim, cap);
this.hb = hb;
this.offset = offset;
}
Buffer(int mark, int pos, int lim, int cap) { // package-private
if (cap < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative capacity: " + cap);
this.capacity = cap;
limit(lim);
position(pos);
if (mark >= 0) {
if (mark > pos)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("mark > position: ("
+ mark + " > " + pos + ")");
this.mark = mark;
}
}
put()
在调用allocate方法分配内存、返回了实例对象后,缓冲区实例对象处于写模式,可以写入对象。要写入缓冲区,需要调用put方法。put方法很简单,只有一个参数,即为所需要写入的对象。不过,写入的数据类型要求与缓冲区的类型保持一致。
ByteBuffer#put(byte b)源码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public abstract ByteBuffer put(byte b);
//byte写入数组,position递增
public ByteBuffer put(byte x) {
hb[ix(nextPutIndex())] = x;
return this;
}
final int nextPutIndex() { // package-private
if (position >= limit)
throw new BufferOverflowException();
return position++;
}
flip()
反转此缓冲区。使Buffer由写入模式转成读取模式。
- 设置可读的长度上限limit。将写模式下的缓冲区中内容的最后写入位置position值,作为读模式下的limit上限值。
- 把读的起始位置position的值设为0,表示从头开始读。
- 清除之前的mark标记,因为mark保存的是写模式下的临时位置。在读模式下,如果继续使用旧的mark标记,会造成位置混乱。
1 2 3 4 5 6
public final Buffer flip() { limit = position; position = 0; mark = -1; return this; }
get()
读取此缓冲区当前位置的字节,然后该位置递增。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public abstract byte get();
public byte get() {
return hb[ix(nextGetIndex())];
}
final int nextGetIndex() { // package-private
if (position >= limit)
throw new BufferUnderflowException();
return position++;
}
rewind()
倒带:重新读取缓冲区,位置被设置为零,并且标记被丢弃。
- position重置为0,所以可以重读缓冲区中的所有数据。
- limit保持不变,数据量还是一样的,仍然表示能从缓冲区中读取多少个元素。
- mark标记被清理,表示之前的临时位置不能再用了。
1 2 3 4 5
public final Buffer rewind() { position = 0; mark = -1; return this; }
mark()和reset()
Buffer.mark()方法的作用是将当前position的值保存起来,放在mark属性中,让mark属性记住这个临时位置;之后,可以调用Buffer.reset()方法将mark的值恢复到position中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public final Buffer mark() {
mark = position;
return this;
}
public final Buffer reset() {
int m = mark;
if (m < 0)
throw new InvalidMarkException();
position = m;
return this;
}
clear()
在读取模式下,调用clear()方法将缓冲区切换为写入模式。此方法会将position清零,limit设置为capacity最大容量值,可以一直写入,直到缓冲区写满。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
//Clears this buffer. The position is set to zero, the limit is set to the capacity, and the mark is discarded.
public final Buffer clear() {
position = 0;
limit = capacity;
mark = -1;
return this;
}
compact()
压缩缓冲区。缓冲区当前位置和界限之间的字节,如果有的话,将被复制到缓冲区的开始。 即,在索引p字节= 位置()被复制到索引0,在索引p + 1的字节被复制到索引1,依此类推,直到将索引limit()的字节- 1被复制到索引n = 极限() - 1 - p。 缓冲区的位置然后被设置为n + 1,并将其界限设置为它的容量。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public abstract ByteBuffer compact();
public ByteBuffer compact() {
System.arraycopy(hb, ix(position()), hb, ix(0), remaining());
position(remaining());
limit(capacity());
discardMark();
return this;
}
小结
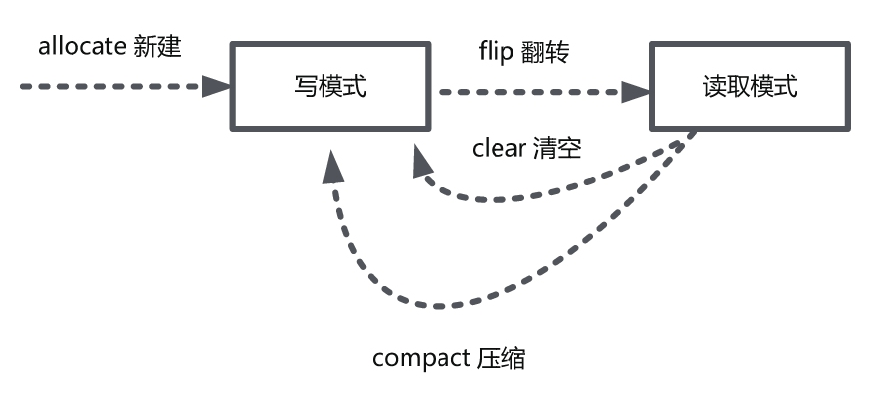
使用Java NIO Buffer类的基本步骤:
- 使用创建子类实例对象的allocate()方法,创建一个Buffer类的实例对象。
- 调用put()方法,将数据写入到缓冲区中。
- 写入完成后,在开始读取数据前,调用Buffer.flip()方法,将缓冲区转换为读模式。
- 调用get()方法,从缓冲区中读取数据。
- 读取完成后,调用Buffer.clear()或Buffer.compact()方法,将缓冲区转换为写入模式。