Java中的BIO->NIO->AIO
Java中支持三种IO模型,分别是BIO、NIO和AIO。
Java BIO
Java中的BIO基于ServerSocket和Socket实现,服务端接收到一个连接就启动一个线程来处理这个连接的所有请求。
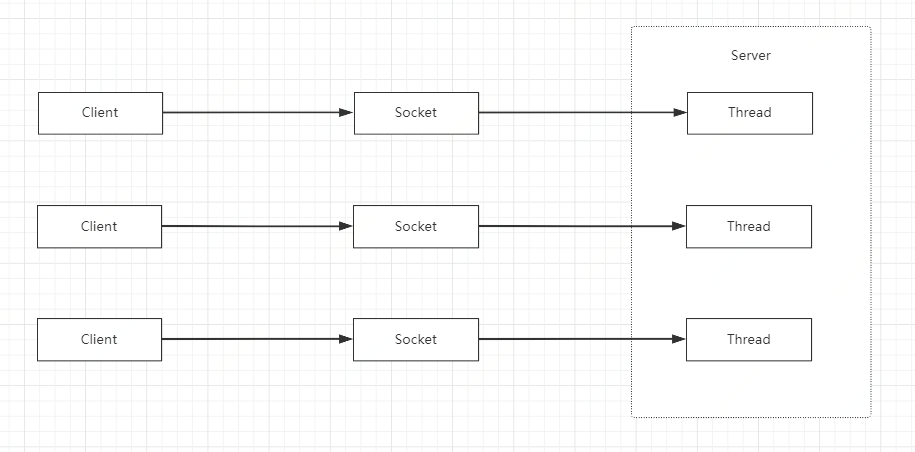
示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public class BioTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
while (true){
System.out.println("start accept");
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("new conn: " + socket.getRemoteSocketAddress());
new Thread(()->{
try {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String str = "";
while ((str=bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){
if(str.equals("exit")){
bufferedReader.close();
socket.close();
break;
}else{
System.out.println(str);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}
}
Java NIO
Java NIO基于多路复用IO模型,使用ServerSocketChannel、SocketChannel、Selector和Buffer缓冲区实现。
使用NIO多条连接的数据准备阶段会阻塞在select上,数据从内核空间拷贝到用户空间依然是阻塞的。
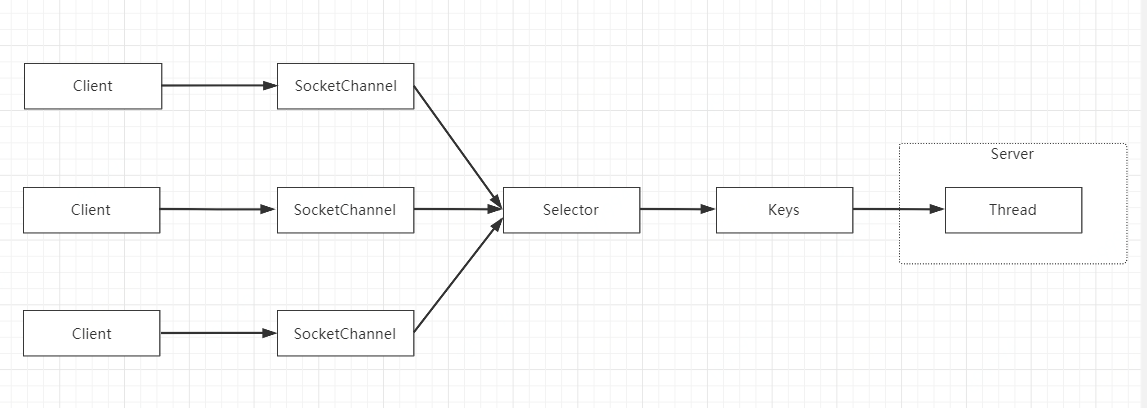
示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
public class NioTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while (true){
selector.select();
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator= selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
{
if(selectionKey.isAcceptable()){
ServerSocketChannel ssc = (ServerSocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
try {
SocketChannel socketChannel = ssc.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else if(selectionKey.isReadable()){
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
try {
int length = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
if(length>0){
byteBuffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[byteBuffer.remaining()];
byteBuffer.get(bytes);
String content = new String(bytes,"UTF-8").replace("\r\n", "");
if(content.equals("exit")){
selectionKey.cancel();
socketChannel.close();
}else{
System.out.println(content);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
Java AIO
使用异步IO则会在请求时立即返回,并在数据已准备且已拷贝到用户空间后进行回调处理,两个阶段都不会阻塞。基于AsynchronousServerSocketChannel、AsynchronousSocketChannel和Buffer缓冲区实现。
示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
public class AioTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
AsynchronousServerSocketChannel asynchronousServerSocketChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open();
asynchronousServerSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
asynchronousServerSocketChannel.accept(null, new CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, Object>() {
@Override
public void completed(AsynchronousSocketChannel socketChannel, Object attachment) {
try {
System.out.println("accept new conn: " + socketChannel.getRemoteAddress());
asynchronousServerSocketChannel.accept(null,this);
while (true){
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Future<Integer> future = socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
if(future.get()>0){
byteBuffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[byteBuffer.remaining()];
byteBuffer.get(bytes);
String content = new String(bytes,"UTF-8");
if (content.equals("\r\n")) {
continue;
}
if (content.equalsIgnoreCase("exit")) {
socketChannel.close();
break;
} else {
System.out.println("receive msg: " + content);
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void failed(Throwable exc, Object attachment) {
System.out.println("faild");
}
});
System.in.read();
}
}