Semaphore
简介
JDK注释:
A counting semaphore. Conceptually, a semaphore maintains a set of permits. Each {@link #acquire} blocks if necessary until a permit is available, and then takes it. Each {@link #release} adds a permit, potentially releasing a blocking acquirer.
However, no actual permit objects are used; the {@code Semaphore} just keeps a count of the number available and acts accordingly
翻译:
Semaphore是一个计数信号量。- 从概念上理解,
Semaphore包含一组许可证。 - 如果有需要的话,每个
acquire()方法都会阻塞,直到获取一个可用的许可证。 - 每个
release()方法都会释放持有许可证的线程,并且归还Semaphore一个可用的许可证。 - 然而,实际上并没有真实的许可证对象供线程使用,
Semaphore只是对可用的数量进行管理维护。
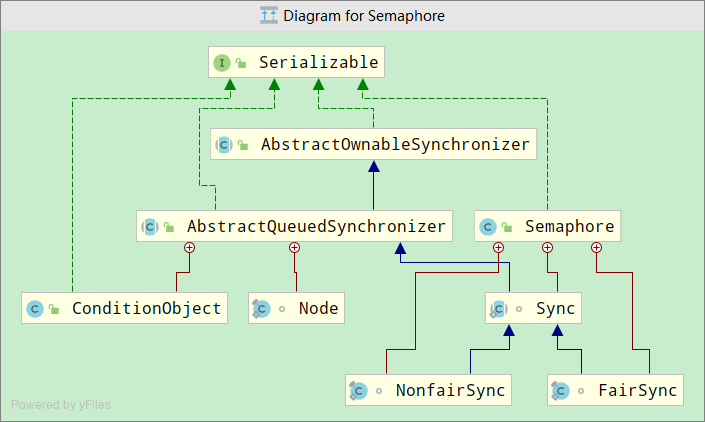
原理
类图
使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
//初始化5个许可证
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(5);
//获取一个许可
semaphore.acquire();
//释放一个许可
semaphore.release();
源码
构造函数
Semaphore提供了两个构造函数:
Semaphore(int permits):创建具有给定的许可数和非公平的 Semaphore。Semaphore(int permits, boolean fair):创建具有给定的许可数和给定的公平设置的 Semaphore。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
//默认非公平 public Semaphore(int permits) { sync = new NonfairSync(permits); } //根据传入是否公平决定 public Semaphore(int permits, boolean fair) { sync = fair ? new FairSync(permits) : new NonfairSync(permits); } //NonfairSync和FairSync构造函数调用的是Sync的构造函数 //本质是设定AQS.state等于传入的许可数。 Sync(int permits) { setState(permits); }
信号量获取
信号量获取的方法分别是: acquire方法| 本质调用 —|—
acquire()|sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(1)acquire(int permits)|sync.acquireSharedInterruptibly(permits)acquireUninterruptibly()|sync.acquireShared(1)acquireUninterruptibly(int permits)|sync.acquireShared(permits);
acquire()方法就相当于AQS.acquireShared(int arg)和AQS.acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg),tryAcquireShared(arg)由子类实现,是主要差异。
非公平锁
Semaphore.NonfairSync#tryAcquireShared()源码:
1
2
3
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquireShared(acquires);
}
Semaphore.Sync#nonfairTryAcquireShared()源码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
//自旋+CAS,返回剩余许可数
final int nonfairTryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
for (;;) {
int available = getState();
int remaining = available - acquires;
//成功的修改了state值,并返回state的剩余值。
//如果剩下的信号量不够了,则就不需要进行CAS操作,直接返回剩余值。
if (remaining < 0 ||
compareAndSetState(available, remaining))
return remaining;
}
}
//获取共享锁,响应中断
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
//如果不能获取到足够的许可,加入共享锁队列
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
公平锁
Semaphore.FairSync#tryAcquireShared()源码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
//与公平锁相比多了判断自己前边是否存线程
protected int tryAcquireShared(int acquires) {
for (;;) {
if (hasQueuedPredecessors())
return -1;
int available = getState();
int remaining = available - acquires;
if (remaining < 0 ||
compareAndSetState(available, remaining))
return remaining;
}
}
信号量释放
Semaphore.release()源码:
1
2
3
public void release() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
Semaphore.release(int permits) 源码
1
2
3
4
public void release(int permits) {
if (permits < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
sync.releaseShared(permits);
}
release()和release(int permits)调用的是AQS.releaseShared(),tryReleaseShared由子类Sync实现。
Semaphore.Sync#tryReleaseShared()源码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
//释放信号量把释放的许可加回
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int releases) {
for (;;) {
int current = getState();
int next = current + releases;
if (next < current) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum permit count exceeded");
if (compareAndSetState(current, next))
return true;
}
}
tryAcquire
尝试获取许可,返回是否成功,不会加入队列阻塞等待,源码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public boolean tryAcquire() {
//调用非公平获取许可
return sync.nonfairTryAcquireShared(1) >= 0;
}
public boolean tryAcquire(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
//现在获取成功则返回成功,否则在队列中等待指定时间
return sync.tryAcquireSharedNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
public boolean tryAcquire(int permits)
public boolean tryAcquire(int permits, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
reducePermits
减少指定的许可,不会进入队列阻塞等待
1
2
3
4
protected void reducePermits(int reduction) {
if (reduction < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
sync.reducePermits(reduction);
}
Semaphore.Sync#reducePermits()源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
final void reducePermits(int reductions) {
for (;;) {
int current = getState();
int next = current - reductions;
if (next > current) // underflow
throw new Error("Permit count underflow");
if (compareAndSetState(current, next))
return;
}
}
drainPermits
将剩下的许可一次性消耗光,并且返回所消耗的许可数量。
1
2
3
public int drainPermits() {
return sync.drainPermits();
}
Semaphore.Sync#drainPermits()源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
final int drainPermits() {
for (;;) {
int current = getState();
if (current == 0 || compareAndSetState(current, 0))
return current;
}
}
示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
public class SemaphoreTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parking parking = new Parking(2);
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
new Car(parking).start();
}
}
static class Parking{
private Semaphore semaphore;
Parking(int count){
semaphore = new Semaphore(count);
}
public void park(){
try {
semaphore.acquire();
long time = (long)(Math.random() * 10);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "进入停车场,停车" + time + "秒..." );
Thread.sleep(time);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开出停车场...");
}catch (Exception e){
}finally {
semaphore.release();
}
}
}
static class Car extends Thread{
private Parking parking;
Car(Parking parking){
this.parking = parking;
}
@Override
public void run() {
parking.park();
}
}
}
结果: